Alcohol Dependency Statistics: Latest Trends
Unveiling the latest alcohol dependency statistics: Stay informed about the trends shaping addiction.
Alcohol Dependency Statistics
Examining the latest trends in alcohol dependency statistics provides valuable insight into the prevalence and severity of Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD).

Prevalence of Alcohol Use Disorder
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a major public-health concern. The 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health revealed that in 2021:
- About 28.8 million U.S. adults (18 and older), or 11.2% of this age group, had AUD.
- Roughly 753,000 adolescents (ages 12-17), or 2.9% of this age group, experienced AUD.
%252520in%252520the%252520United%252520States.jpeg)
%252520in%252520U.S.%252520adolescents.jpeg)
Severity Levels of Alcohol Use Disorder
The severity of AUD is determined by the number of criteria a person meets based on their symptoms. These criteria cover various aspects of alcohol consumption and its impact on an individual's life. AUD severity levels are:
- Mild: 2-3 criteria met
- Moderate: 4-5 criteria met
- Severe: 6 or more criteria met
Understanding AUD's prevalence and severity is crucial for gauging the scope of the issue and developing effective strategies for prevention, intervention, and treatment.
For more statistics on addiction and related topics, you can refer to our articles on anxiety disorders - facts & statistics, current addiction statistics 2024, opioid addiction statistics: current trends, and internet addiction statistics: latest data.
Treatment Options for Alcohol Dependency
When it comes to addressing alcohol dependency, there are various treatment options available to help individuals on their journey to recovery. These options include medications, behavioral treatments, and the role of mutual-support groups.
Medications for Treating AUD
Medications can play a crucial role in the treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD). Three medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to assist individuals in stopping or reducing their drinking and preventing a relapse: naltrexone (both oral and long-acting injectable forms), acamprosate, and disulfiram. These medications are non-addictive and can be used alone or in combination with other treatment approaches.
Medication Purposes:
- Naltrexone
- Reduces alcohol cravings
- Blocks the pleasurable effects of alcohol
- Acamprosate
- Helps individuals maintain abstinence
- Reduces the unpleasant symptoms of withdrawal
- Disulfiram
- Causes unpleasant physical reactions when alcohol is consumed
- Acts as a deterrent
It's important to note that medication should be prescribed and monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective use.
Behavioral Treatments for AUD
Behavioral treatments are another essential component of alcohol dependency treatment. These treatments involve working with licensed therapists who provide various interventions and strategies to address AUD. Some common behavioral treatments include:
- Brief interventions: These short-term counseling sessions aim to motivate individuals to change their drinking behaviors and provide them with practical coping strategies.
- Reinforcement approaches: Techniques such as incentives and rewards are used to reinforce positive behaviors, such as maintaining abstinence or reducing alcohol consumption.
- Treatments that build motivation: Therapists help individuals explore their reasons for change and work on enhancing their motivation to overcome alcohol dependency.
- Coping skills training: Individuals learn effective strategies to manage triggers, stress, and other challenges without resorting to alcohol use.
- Mindfulness-based therapies: Techniques such as mindfulness meditation and acceptance-based practices are utilized to increase self-awareness and promote healthier coping mechanisms.
These behavioral treatments are tailored to the individual's specific needs and may be provided in individual or group settings.
Role of Mutual-Support Groups
Mutual-support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), can provide valuable peer support and a sense of community for individuals seeking to recover from alcohol dependency. These groups offer an additional layer of support when combined with medications and behavioral treatments provided by healthcare professionals.
In mutual-support groups, individuals can share their experiences, receive encouragement, and learn from others who have successfully overcome alcohol dependency. Attending these meetings can help individuals build a supportive network and gain insights into long-term recovery.
It's worth noting that mutual-support groups are not a substitute for professional treatment, but they can be a valuable complement to other forms of treatment.
By combining medications, behavioral treatments, and the support of mutual-support groups, individuals with alcohol dependency can access a comprehensive range of resources to aid in their recovery journey. It's important to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most effective treatment approach based on individual needs and circumstances.
Regional Variances in Alcohol Dependency
Alcohol dependency is a global concern, with regional variations in its prevalence and impact. In this section, we will explore the alcohol dependency statistics in England and the United States.
Alcohol Dependency in England
In England, alcohol consumption is a significant public health issue. According to a study by the NCBI Bookshelf:
- 24% of adults consume alcohol in a potentially or actually harmful way
- 4% of adults are classified as alcohol dependent
- 6% of men
- 2% of women
Regional variations in alcohol dependence prevalence:
- In 2000, 4% of 16- to 64-year-old adults were alcohol dependent
- By 2007, this increased to 1.6 million people
- Prevalence ranged from 2% in the East Midlands to 5% in the North West
Alcohol-related hospital admissions:
- Increased by 85% between 2002/03 and 2008/09
- In 2008/09, there were 945,000 admissions with alcohol as a primary or secondary diagnosis
- Most prevalent in the 60- to 64-year-old age group
Alcohol Dependency in the US
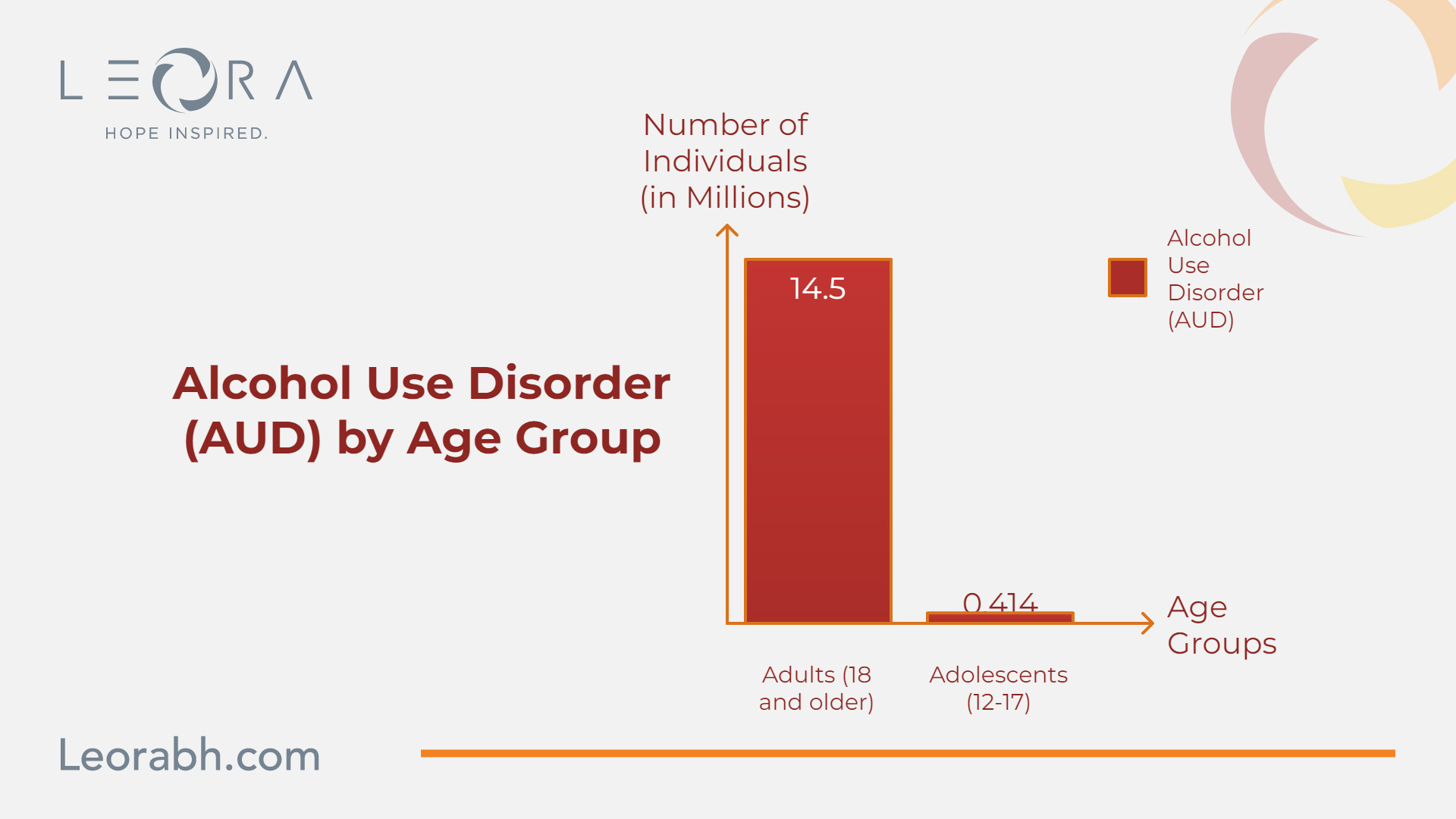
The United States also faces significant challenges related to alcohol dependency. While specific data for Ohio is not available, national statistics provide insight:
According to the NCBI Bookshelf and the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) in 2019:
- 14.5 million adults (18 and older) had Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD)
- 5.8% of the adult population
- 414,000 adolescents (12-17) had AUD
Alcohol dependency varies across demographics and regions within the United States due to local factors, cultural influences, and socioeconomic disparities. For Ohio-specific data, refer to local research and resources.
Understanding regional variances in alcohol dependency highlights the issue's magnitude and informs targeted interventions and support systems. By addressing unique regional challenges, we can work towards reducing alcohol dependency's impact and improving individual and community well-being.
Vulnerabilities and Risk Factors
When examining alcohol dependency, it is important to understand the vulnerabilities and risk factors that contribute to the development of alcohol dependence. Two significant factors to consider are the genetic component in alcohol dependence and the impact of family history on alcohol involvement.
Genetic Component in Alcohol Dependence
Studies have shown that substance dependence, including alcohol dependence, has a substantial genetic component in various populations. In Native American populations, for example, research has indicated a genetic susceptibility to substance dependence, similar in magnitude to that reported for other populations. Heritability estimates for alcohol dependence in Native American populations range from 0.19 to 0.38 for DSM-III-R and DSM-IV criteria.
Twin studies conducted on predominantly Caucasian populations have consistently shown significant evidence of heritability for alcohol dependence, with estimates ranging from 0.50 to 0.65. These findings suggest that genetic factors play a role in the development of alcohol dependence.
Genome scans conducted in Native Americans have identified specific chromosomal regions associated with alcohol dependence. These regions include chromosomes 11p15.5, 4p11-p13, 4q23-q25, 5q21.2-q21.3, 4q22.1, 12q24.32, 6p21.1, 15q22.2-q25.3, 16p13.3, 16q24.1, and 19q13.33. Moreover, candidate gene studies have identified associations between alcohol and other drug dependence phenotypes and genes such as ADH1B, ADH4, ALDH1A1, CNR1, GABRA2, GABRG1, OPRM1, CRN1, COMT, MAOA, and HTR3-B, further supporting the genetic component in substance misuse disorders [2].
Impact of Family History on Alcohol Involvement
Family history of alcoholism can also significantly influence an individual's susceptibility to alcohol involvement, particularly during adolescence. Cognitive social learning theory suggests that youth form beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors based on what they observe in the home. This includes the use and effects of alcohol, which are shaped by parental modeling. Consequently, the cognitive schema regarding alcohol, known as alcohol expectancies, are influenced by the family environment and can contribute to an increased risk of alcohol involvement.
Understanding the genetic component and the influence of family history on alcohol involvement is essential for recognizing potential vulnerabilities to alcohol dependency. However, it's important to note that genetic predisposition or family history alone does not determine an individual's fate. Environmental factors, social influences, and personal choices also shape an individual's relationship with alcohol. By recognizing these vulnerabilities and understanding the risk factors, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to prevent and address alcohol dependency.
Alcohol Dependence Across Age Groups
Alcohol dependency and consumption patterns can vary across different age groups. Understanding the statistics related to alcohol use among youths and different age brackets is essential for developing targeted prevention and intervention strategies.
Youth Alcohol Consumption Statistics
According to the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health:
- About 7% of youths aged 12-17 reported drinking alcohol in the past month
- Roughly 3.2% engaged in binge drinking during the same period NIAAA
Binge drinking episodes are considered a marker for dangerous alcohol use among youth NCBI.
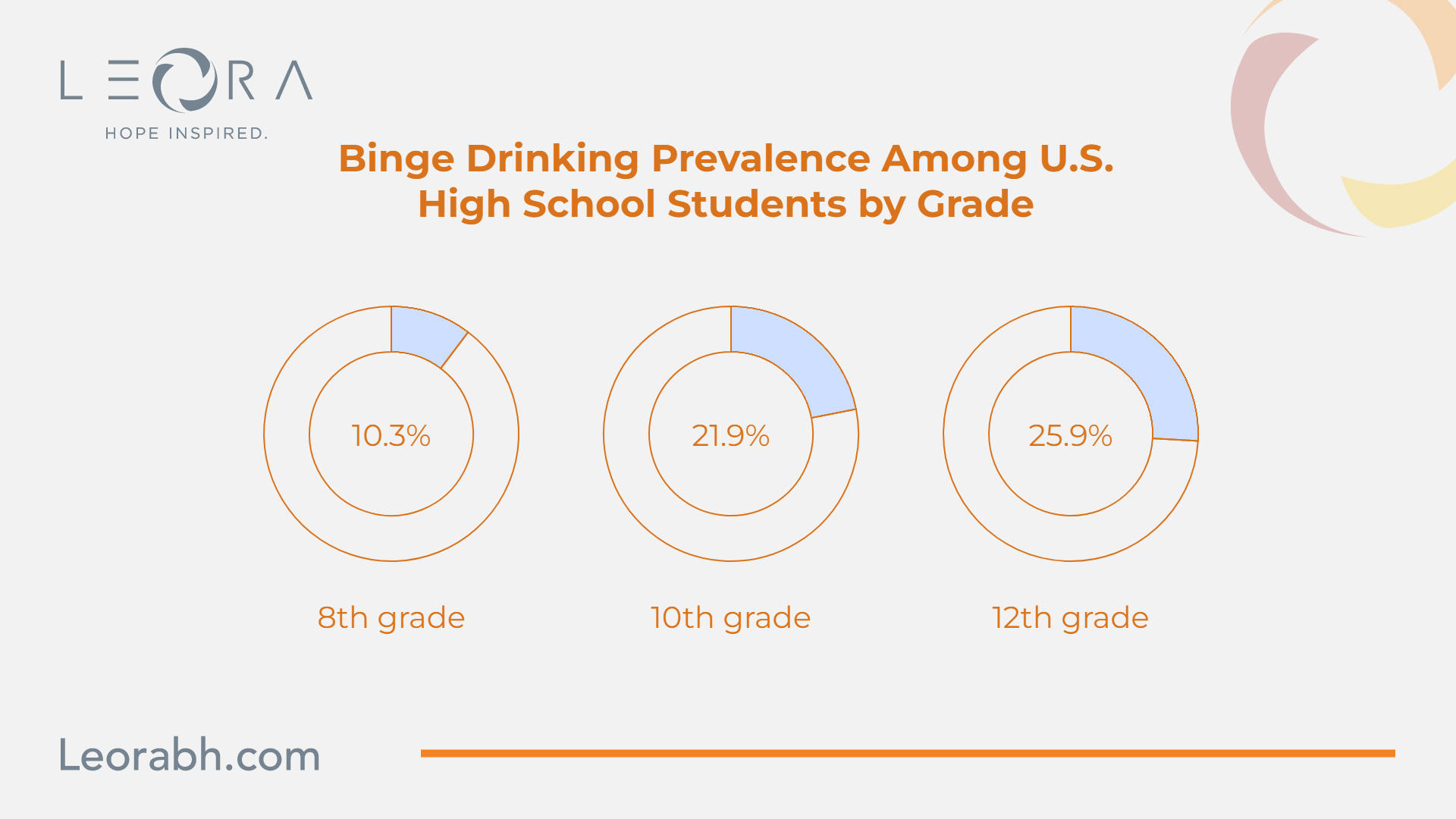
Binge drinking prevalence among U.S. high school students increases by grade:
- 8th grade: 10.3%
- 10th grade: 21.9%
- 12th grade: 25.9%
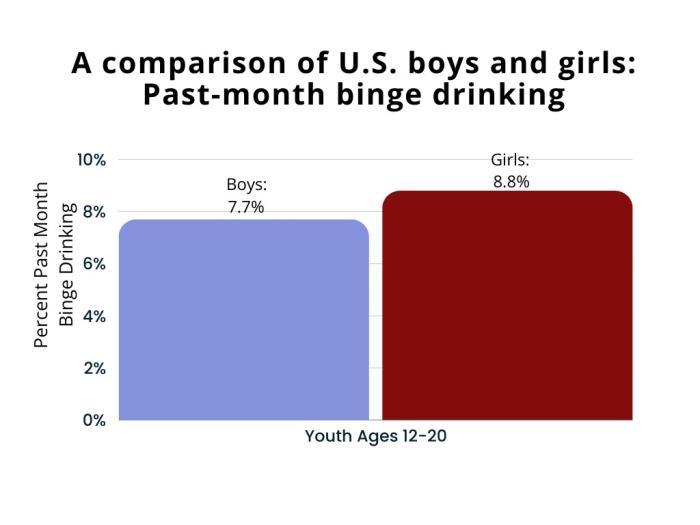
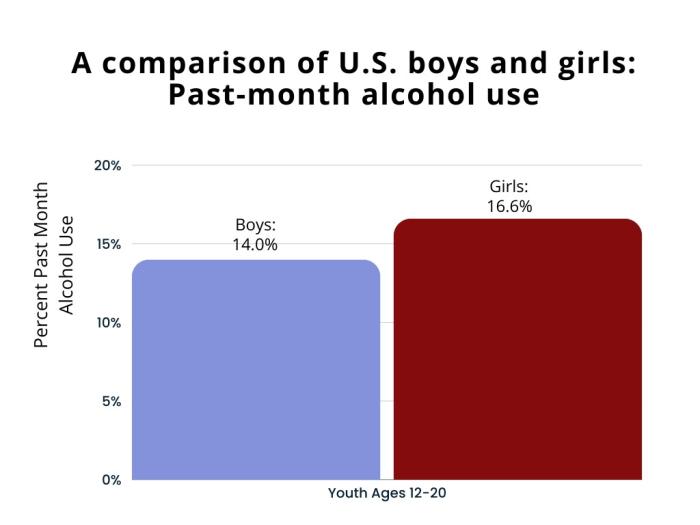
Experimental drinking rates don't differ significantly by gender for ages 12-18. However, gender differences in Alcohol Use Disorders (AUDs) emerge around age 18 NCBI.
Alcohol Dependency Trends in Different Age Groups
For young adults aged 18-25:
- About 50% reported alcohol use in the past month
- Around 60% of those drinkers engaged in binge drinking
- Approximately 1 in 6 had an Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD)
Among binge drinkers:
- Alcohol dependence rates were higher in men (11.1%) than women (9.7%)
- Dependence was highest in the 18-24 age group and decreased with age
These statistics emphasize the importance of addressing alcohol dependency and promoting responsible drinking behaviors among youths and different age groups. Strategies focused on prevention, education, and early intervention can help mitigate the risks associated with alcohol consumption across various age brackets. For more information on alcohol dependency statistics and related topics, please visit our articles on anxiety disorders - facts & statistics, current addiction statistics 2024, opioid addiction statistics: current trends, and internet addiction statistics: latest data.
Gender Disparities in Alcohol Consumption
When examining alcohol consumption patterns, it is important to consider the historical trends and current patterns that exist between genders. Historically, men have had higher rates of alcohol consumption, alcohol-related consequences, and Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) than women. However, in recent years, the gender gap in heavy drinking and alcohol problems has noticeably narrowed, with trends in alcohol use varying by age group.
Historical Gender Trends in Alcohol Use
In the past, men have consistently exhibited higher rates of alcohol consumption compared to women. This gender disparity was evident in various measures, including binge drinking and rates of AUD. Among binge drinkers, the prevalence of alcohol dependence was significantly higher among men (11.1%) than among women (9.7%). Furthermore, the rates of alcohol dependence were highest among binge drinkers aged 18 to 24 and decreased significantly with increasing age [5].
Current Gender Patterns in Alcohol Problems
While men still tend to have higher rates of alcohol consumption overall, there has been a shift in recent years. Rates of alcohol consumption, binge drinking, and alcohol-related harms are increasing at a faster rate for women than men in middle and older adulthood. The narrowing gender gap suggests an increased vulnerability for women in terms of problematic alcohol use. It is important to note that rates of experimental drinking among American youth ages 12 to 18 do not differ by gender. However, boys and girls only begin to diverge in rates of Alcohol Use Disorders (AUDs) around age 18, with symptom profiles demonstrating gender-specific patterns.
Additionally, when considering socioeconomic factors, binge drinking was found to be most common among those with annual family incomes of $75,000 or more, whereas alcohol dependence was most common among those with annual family incomes of less than $25,000 [5].
Understanding the gender disparities in alcohol consumption is essential for tailoring prevention efforts and providing appropriate support and treatment to those in need. By recognizing the specific challenges faced by different gender groups, interventions can be better designed to address the unique needs and risks associated with alcohol use across genders. For more information on addiction statistics and trends, you can refer to our articles on current addiction statistics 2024 and opioid addiction statistics: current trends.
References
Find Your Inner Light
Related Articles
Contact Us
Leora Behavioral Health offers a comprehensive addiction treatment programs to help you get your life back on track.
Our trained professionals will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your unique needs. If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, reach out to Leora Behavioral Health today.


.svg)





.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)